Languages are often the privileged witnesses of the cultural melting pot that shapes a country. Thus, the French language multiplies its legacies: from Latin to Greek through Arabic or even English.
Conversely, the language of Molière also influenced foreign languages, this being due in particular to French colonialism but not only. Cultural exchanges leave traces and are thus found in the different linguistic strata of each country.
Vietnamese is no exception. Let’s have a quick overview of the influences of the French language on Vietnamese!
Table of Contents
ToggleA bit of History
It was in 1861 that the French extended their colonial empire to Cochinchina. But the presence of the French in this region of Southeast Asia dates from the 18th century, the time of the first repeated commercial exchanges between the two peoples. It was even the French who helped Emperor Nguyen to unify Vietnam, thus becoming the region’s first European influence, ahead of Portugal.
But it was only at the time of the conquest of southern present-day Vietnam that the French language was imposed, a language that would remain dominant under French colonization until the Geneva Agreements. Therefore, young Vietnamese must learn French, which imposes itself on the royal court at the expense of Chinese and Vietnamese. The missionaries installed on the territory took care of building schools and institutions responsible for transmitting French culture among the populations. French thus became the language spoken by the Vietnamese elites at the end of the XIXth century which undoubtedly constitutes the apogee of the French influence on Vietnam.
This influence began to diminish during the Second World War when protest movements declared themselves in favor of Vietnam’s independence. Many groups refused to speak French and they quickly came to publish in Vietnamese.
Vietnamese is part of the Mon-Khmer language group of Austro-Asian origin. It is a so-called isolating language: in fact, all the words it contains remain invariable, no matter how they are used, like Chinese. This language has 6 tones, that is to say, 6 different ways to accentuate the word. A particularity that makes its learning quite difficult for French speakers who are not used to these vocal nuances. Beyond that, these two languages continue to have close ties. Thus, the centuries of French influence have deeply marked the Vietnamese language, so much so that many Vietnamese words come directly from French.
Learn Vietnamese thanks to the French language?
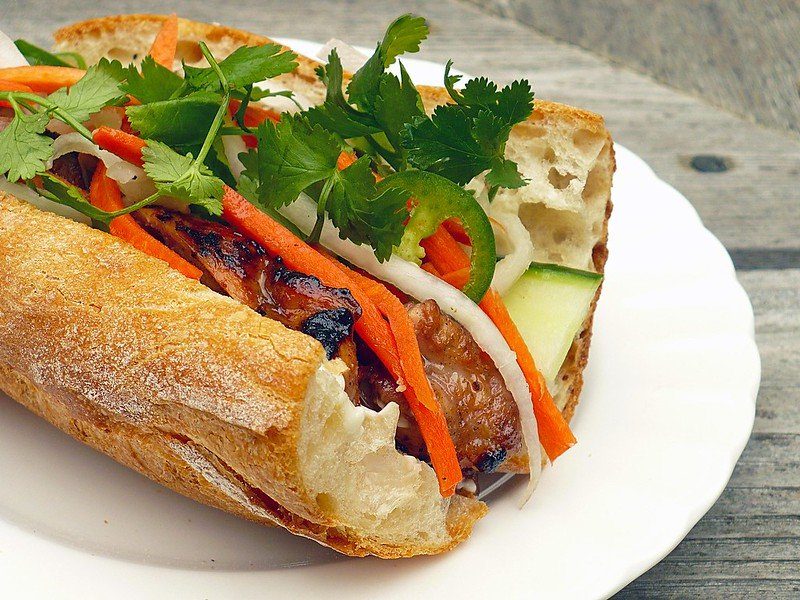
The French installation in Cochinchina and more particularly in Vietnam was accompanied by a development of infrastructures, economy, and industry. Thus, the French who settled in Vietnam sought both to develop the territory but also to establish their culture of origin there. French influence is thus found through certain transparent words which testify to the cultural sharing that took place between the two peoples. At the forefront of these exchanges: gastronomic exchanges of course. Many specialties or products have been introduced in Vietnam by the French and that is why we still find many French words that have been the subject of a kind of Vietnamization.
Thus, the famous Banh Mi or even Ca Phe are nothing other than Bread and Coffee that the French brought with them. Xuc Xich is none other than the traditional sausage! The Vietnamese phô is thus a revisited version of the famous stew “pot au feu”. You can therefore go to Vietnam and make yourself understood by ordering your breakfast or dinner if you know a bit of French! The techniques are not to be outdone. Thus, you can cross Vietnam on your mô tô or comfortably installed in your ô tô, two other French words. The vocabulary specific to the use of the telephone is also of French origin, so do not be surprised to hear a Vietnamese say alô by picking up his phone. These are a whole set of terms from gastronomy, technology, or more simply from objects imported by the French that are found in the Vietnamese language and which will give you the impression of a certain familiarity.

It is Alexandre de Rhodes, an Avignonese Jesuit who gave the Vietnamese his alphabet, thus making it pass from its form in ideograms to Quoc Ngu, which is the romanized version, that is to say, calibrated on the Latin alphabet. Thus, unlike the other languages of the continent, Vietnamese presents a serious advantage for Westerners as it is written in the same alphabet. If the accent is different and therefore always presents a difficulty for expatriates, it remains much easier than other languages like Japanese or Chinese.
The future of the French language in Vietnam
That said, French influence in Vietnam is struggling to regain its former glory.
And for good reasons, in the economy, it is the English language that dominates. A conclusion was shared by Nicole Bricq during a visit to Ho-Chi-Minh in April 2013. The Minister of Foreign Trade then expressed the wish to double the market share of French companies in Vietnam. If the objective has not been fully achieved, there is a certain influence of the French in Vietnam, this due in particular to the increase in the number of expatriates in Vietnam. Thus, the economic field is a privileged battlefield for the French who must succeed in rebuilding their place in Vietnamese society.
But this decrease in the number of French speakers in Vietnam is also structural. If there are only 1% of French speakers among the 90 million Vietnamese, it is also because it is a very young population. However, this section of the population has never known French colonization and is even very far from it since it ended in 1954, the date of the withdrawal of French troops. That said, French remains a family tradition within a small circle of the Vietnamese population.
However, the French language is far from having disappeared from Vietnam. In recent years, the demand for enrollment in French courses has continued to increase. Whether to reconnect with a family heritage or because of professional opportunities, French retains a certain aura in Vietnam where we readily recognize that if “English is better for business, French is better to tell a story“.
Finally, what gives good hope are the links that France and Vietnam maintain. Thus, more than 6000 Vietnamese students are enrolled in France, thanks to the much lower costs of education than in Anglo-Saxon countries. This tradition of exchange between the two countries suggests a revival of French in Vietnam, hence the emergence of French specific to expatriates who no longer hesitate to infuse their French with Vietnamese terms.
French – Vietnamese transparent words list
affiche áp phích
absinthe rượu apxanh
acide axit
aiglefin cá êfin
anis cây anit
antenne an-ten
antenne parabolique anten parabôn
artichaut cây atisô
aspirine atpirin
autobus xe buýt
automobile xe ô tô
balcon ban công
ballet ba lê
ballot (sac à dos) ba-lô
bandeau dải vấn đầu
bébé em bé
beurre bơ
bière bia
billes (jeu) bi
biscuit bánh (bich) quy
biftek bít tết
bombe bom
bougie (de moteur) buji
bouillabaisse món buiabet
boulon bu lông
café cà phê
cantine căng tin
caoutchouc cao su*
caramel (flan) caramen
cardan các đăng
cari ca ri
cas ca
chemise áo sơ mi
carotte cà rốt
chartreuse rượu sactrơ
chocolat sô cô la
ciment xi măng
cinéma xi nê
cirque rạp xiếc
cognac rượu cô nhắc
corset coocxê
coup cú
condom (capote, caoutchouc) capốt (vulg.), bao cao su*
cravatte cái ca vát, cà vạt
crème glacée kem
cyan xanh **
cyclo xích lô
dâme đầm
dollar đồng đô la
divan ghế đi văng
drap dạ
épinard rau bi na
essence xăng
(faire la) cour Cưa
fermeture éclair phéc-mơ-tuya
film phim
filtre (à café) phin
frein cái phanh
fromage phô mai, phó mát
gâteau bánh ga-tô
gant găng
gare nhà ga
gilet áo gi lê
gin rượu gin
golf gôn
gomme à effacer gôm
gomme arabique gôm A Rập
guidon ghi đông
guitare đàn ghita
homosexuel (pédéraste) pê đê (vulgaire)
jambon giam bông
jeans quần jean
laine len
lynx mèo linh, linh miêu
manteau măng tô
maquereau ma cô (celui qui pratique le maquerellage)
marmotte con macmôt
mayonnaise nước xốt mayonne
médaille mề đay
mère mẹ
morue cá moruy
moutarde mù tạt
niveau (objet) cái nivô
oeuf au plat op la
noeud papillon nơ
olive cây/quả ôliu
orgue đàn ống
pain (avec mie) bánh mì
paletot bành tô
papier fin (pelure) giấy pơluya
pastis (liqueur d’anis) rượu anit
pâté pa tê
pile (électrique) pin
piston pittông
pompe cái bơm
pourboire tiền buột-boa
poupée púp pê, búp bê
pédale pê đan
pénicilline pê ni xi lin
quai kè, kê
radio rađiô
ragoût món ragu
rhum rượu rom
sac Tui xách
salade rau xà lách
club sandwich xăngđuýt
saucisse xúc xích
savane xavan
savon xà phòng, xà bòng
sirop xi rô
soupe xúp
soupe tonkinoise (de pot-au-feu) phở (incertain)
soutien-gorge cái xu chiêng
tape cái tát
tasse cái tách
taxi xe tắc xi
timbre tem
tournevis cái tuanơvit
veston áo vét tông
valse van
valve van
vanne van
vin rượu vang
vis vít
vison chồn vizon
valise cái va li
vodka rượu votca
whiskey rượu uytky
zéro cê-rô, zé ro
Sources :